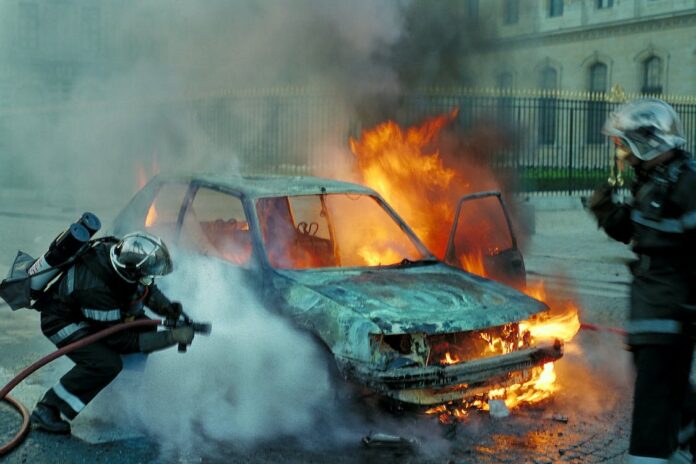
Aqueous film-forming foam (AFFF), a potent firefighting tool, now stands at the center of a growing environmental crisis. This foam contains toxins, which have raised significant concerns due to their persistence and harmful effects.
While AFFF plays a critical role in safeguarding lives and property from fires, its unintended consequences on groundwater quality and aquatic ecosystems are troubling. In this article, we will discuss the multidimensional threats posed by AFFF as an alarming menace to groundwater quality and aquatic ecosystems.
Groundwater Contamination
AFFF, widely used in firefighting, presents a significant threat to groundwater quality. According to the NHDES, when AFFF is applied to extinguish fires, it can lead to the release of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. More popularly known as PFAS, these persistent chemicals gradually seep into the soil and find their way into underground aquifers, contaminating drinking water.
The consequences of this contamination extend far beyond the initial firefighting incident, as PFAS persists in the environment and continues to leach into groundwater. The potential for widespread groundwater contamination is a serious concern, as it jeopardizes the quality of our water sources.
Impact on Aquatic Ecosystems
Aquatic ecosystems are particularly vulnerable to the consequences of AFFF contamination. PFAS, known for their resistance to degradation, can accumulate in aquatic environments, affecting aquatic life and the delicate balance of ecosystems.
These persistent chemicals can disrupt the food chain, with potential harm to fish, amphibians, and other aquatic organisms. Moreover, the introduction of PFAS into aquatic habitats can have far-reaching ecological effects. This impacts both individual species and the overall health of aquatic ecosystems.
According to the NIH, PFAS can accumulate in the bodies of aquatic species and cause a number of harmful effects. Reproductive toxicity, oxidative stress, metabolic disturbance, immunological toxicity, developmental toxicity, cellular destruction, and necrosis are all examples of this.
Human Health Concerns
The PFAS present in AFFF not only pose threats to groundwater and aquatic ecosystems but also have severe health implications for humans. Prolonged exposure to these chemicals has been linked to a range of health problems. This includes increased risk of cancer, immune system dysfunction, changes in fetal development, and cholesterol abnormalities.
Furthermore, long-term exposure to AFFF can lead to liver damage, fertility issues, thyroid disease, and ulcerative colitis. These health concerns underline the pressing need to address the use of AFFF and its potential for human harm.
Legal Actions and Accountability
In response to the growing awareness of AFFF’s risks, legal actions are being taken against manufacturers. According to TruLaw, these Afff lawsuits highlight the need for accountability in addressing the environmental and health consequences of AFFF.
Manufacturers are being held responsible for their alleged failure to adequately warn the public about the dangers of PFAS in AFFF. The AFFF lawsuit aims to seek justice for those affected by AFFF-related health problems and to promote transparency in the use of firefighting foams.
According to a recent update by Reuters, defendant 3M has reached a proposed settlement to pay an amount of $10.3 billion. If approved, the payout will settle a lot of AFFF cases in the coming years. This settlement comes as DuPont, Chemours, and Corteva have also agreed to pay $1.185 billion in AFFF cases.
Drinking Water Contamination
Communities located in the vicinity of areas where AFFF is used may face contamination of their drinking water sources. This contamination intensifies the urgency of addressing the issue.
PFAS chemicals can infiltrate public water supplies, putting residents at risk of exposure to these harmful substances through daily consumption. The potential for AFFF-related contamination of drinking water further underscores the need for comprehensive and immediate action.
Environmental Conservation
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of AFFF involve the conservation of groundwater and aquatic ecosystems. Sustainable firefighting practices and alternatives are being explored to reduce the reliance on AFFF and minimize its adverse effects on the environment. Promoting responsible firefighting practices and adopting environmentally friendly alternatives can contribute to the protection of our natural resources.
Collaborative Solutions
Addressing the alarming threats posed by AFFF requires collaborative efforts from government agencies, environmental organizations, the firefighting community, and manufacturers. Regulations are being introduced to restrict the use of AFFF and PFAS in firefighting equipment, promoting safer alternatives.
Ongoing research and the exchange of knowledge are crucial for identifying effective solutions that protect groundwater quality and aquatic ecosystems. Collaboration is key to safeguarding these vital resources and preserving the health of both our environment and our communities.
Ending Note
Aqueous film-forming foam (AFFF) is undeniably an indispensable tool in firefighting, but its unintended consequences on the environment and human health cannot be ignored.
The insidious nature of PFAS chemicals in AFFF demands urgent attention, as they persist in the environment, impacting ecosystems and causing severe health issues. Legal actions are holding manufacturers accountable, highlighting the need for transparency and responsibility.
The risk of drinking water contamination in communities further emphasizes the pressing need for action. Collaborative efforts, regulatory measures, and the exploration of eco-friendly alternatives are imperative to protect our environment and the well-being of our communities.